Research Interests -
Gregory J. Brewer October 23, 2019

We
work at the last frontier of biology, the brain. Our research is directed in two
NIH-supported areas: 1) Determine the coding of memory in engineered live
neuronal networks reconstructed from the hippocampus 2) epigenetic and redox
control of neuron metabolism, aging and Alzheimer disease (AD). We hypothesize that aging is the last
stage of development controlled by epigenetics.
Relevant publications, grouped by research area (last 10 years + a few landmark citations, in numerical order of publication and selectively annotated) (full list of publications: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/gregory.brewer.1/bibliography/public/).
Neuronal Networks (reassembling engineered
connections of live neurons)
29. Corey, J.M.,
Wheeler, B.C., and Brewer, G.J. 1996.
Micrometer resolution silane-based patterning
of hippocampal neurons: critical variables in photoresist and laser ablation
processes for substrate fabrication. IEEE Proc. 43:944-955.PM:9214810
(One of the first demonstrations that
neuron growth could be restricted to arbitrary patterns on a substrate and that
neuronal somata migrate to the nodes).
36. Branch D.W.,
Corey J.M., Weyhenmeyer J.A., Brewer, G.J. and
Wheeler, B.C. 1998. Microstamp
patterns of biomolecules for high-resolution neuronal networks. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 36:135-141.PM:9614762
41. Wheeler, B
C., Corey, J.M., Brewer, G.J. and Branch, D.W. 1999. Microcontact
printing for precise control of nerve cell growth in culture. J. Biomech. Eng. 121:73-78.PM:10080092
48. Branch,
D.W., Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. and Leckband,
D.E. 2000. Long-term maintenance of
patterns of hippocampal pyramidal cells on substrates of polyethylene glycol
and microstamped polylysine. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.
47:290-300.PM:10743770
54. Branch, D.W.,
Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. and Leckband,D.E. 2001. Long-term stability of grafted
polyethylene glycol surfaces for use with microstamped
substrates in neuronal cell culture. Biomaterials
22:1035-1047. PM:11352085
57. Chang, J.C.,
Wheeler, B.C. and Brewer, G.J.
2001. Microelectrode array recordings of patterned hippocampal neurons
for four weeks. Biomedical Microdevices 2:245-253. (Process improvements for long-term
viability).
58. Chang, J.C.,
Brewer, G.J. and Wheeler, B.C.
2001. Modulation of neural
network activity by patterning. Biosensors & Bioelec. 16:527-533.PM:11544046
63. Chang, J.C.,
Brewer, G.J.,Wheeler, B.C.
2003. A Modified Microstamping Technique Enhances Polylysine Transfer and
Neuronal Cell Patterning. Biomaterials 24: 2863-2870.PM:12742724
(Process improvements to improve
reliability).
 64. Nam, Y., Chang,
J.C., Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2004. Gold-coated microelectrode array with thiol linked self-assembled monolayers for engineering
neuronal circuits. IEEE Trans.
Biomed. Eng. 51:158-165. PM:14723505 (Improved
chemical stability of substrate over periods of weeks).
64. Nam, Y., Chang,
J.C., Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2004. Gold-coated microelectrode array with thiol linked self-assembled monolayers for engineering
neuronal circuits. IEEE Trans.
Biomed. Eng. 51:158-165. PM:14723505 (Improved
chemical stability of substrate over periods of weeks).
67. Nam,
Y., J. Chang; D. Khatami; G.J. Brewer; B.C. Wheeler, 2004 Patterning to enhance
activity of cultured neuronal networks. IEEE Proc-Nanobiotechnol
151:109-115. PM: 16475852
68. Khatami,D., Nam,Y., Brewer,G., Wheeler,B. 2004. Effect of
bicuculline on the spontaneous
and evoked activity of patterned embryonic hippocampal neurons cultured in vitro. Conf. Proc. IEEE EMBS 6:4059-4062. PM:17271191
70. Vogt, A.K.,
Brewer, G.J., Decker, T., Boecker-Meffert, S.,
Jacobsen, V., Kreiter, M., Knoll, W., Offenhausser, A. 2005. Independence of
synaptic specificity from neuritic guidance.
Neuroscience., 134:783-790. PM:16009499
(Identifies proportions of excitatory
and inhibitory synapses.)
71. Vogt,A.K.; Brewer,G.J.; Offenhausser,A. 2005.
Connectivity
patterns in neuronal networks of experimentally defined geometry, Tissue Eng, 11:1757-1767.
PM:16411821

73. Chang, J.C., Brewer, G.J, Wheeler, B.C. 2006. Neuronal network structuring induces
greater neuronal activity through enhanced astroglial development, J. Neural
Eng. 3:217-226. PM: 1692105.
76. Rowe, L, Almasri, M., Lee, K., Fogleman, N., Brewer, G.J., Nam, Y., Wheeler, B.B., Vukasinociv, V., Glezer, A.,
Frazier, A.B., 2007. Active 3-D Microscaffold System
with Fluid Perfusion for Culturing in Vitro Neuronal Networks, Lab Chip 7:475-482. PM:17389964 (First 3D patterned growth of
neurons).
77. Boehler, M.D.,
Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2007.
Added astroglia promote greater synapse density and higher activity in
neuronal networks, Neuron Glia Biology 3:127-140. PM:18345351. PMCID: PMC2267743
(Clear role of astroglia to enhance
network firing dynamics).
80. Nam, Y, Brewer,
GJ, Wheeler, BC. 2007. Development
of astroglial cells in patterned neuronal cultures, J. Biomaterials Science,
Polymer Edition 18:1091-1100. PM:17706000
83. Vernekar, V. N., Cullen, D.K., Fogleman,
N, Choi, Y, Garcia, A.J., Allen, M.G., Brewer, G.J., LaPlaca,
M.C. 2008. Cytocompatibility
of SU-8 2000 with primary neuronal cultures, J Biomed Mater Res A 89:138-151. PM:18431778.
 86. Brewer, G.J., Boehler, MD;
Jones, TT, Wheeler, BC. 2008. NbActiv4 medium for neurons increases synaptic
densities and network spike rates on multielectrode
arrays compared to Neurobasal/B27.
J. Neurosci. Meth. 170:181-187. PM:18308400 PMC2393548 (Designed selective
nutrients to enhance synaptogenesis and consequent network dynamics; first
improvement to Neurobasal/B27 in 15 years).
86. Brewer, G.J., Boehler, MD;
Jones, TT, Wheeler, BC. 2008. NbActiv4 medium for neurons increases synaptic
densities and network spike rates on multielectrode
arrays compared to Neurobasal/B27.
J. Neurosci. Meth. 170:181-187. PM:18308400 PMC2393548 (Designed selective
nutrients to enhance synaptogenesis and consequent network dynamics; first
improvement to Neurobasal/B27 in 15 years).
88. Brewer, G. J., Boehler M.D., Pearson, R., DeMaris, A., Wheeler,
B.C. 2009. Neuron Network Activity Scales Exponentially with Synapse Density.
J. Neural. Eng. 6:14001. PM:19104141. PMC2679226 (First indication of a
logarithmic relationship between synapse density and spike rate, relevant to
computational design).
90. Brewer, G.J., Boehler,
M.D., Ide, A.N., Wheeler, B.C. 2009.
Chronic electrical stimulation of cultured hippocampal networks
increases spontaneous spike rates.
J. Neurosci. Meth. 184:
104-109. PM:19666055 PMC2753692.pdf
(Most neuronal networks develop without
external stimulation. A more
natural development with chronic inputs results in a more active network.)
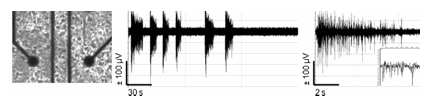
95. Ide, A.N., Andruska,
A., Boehler, M., Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2010.
Chronic network stimulation enhances evoked action potentials, J. Neural Eng.
7, 16008 PM:20083862. PMCID: 20083862
![]()
![]()
103. Boehler, M.D., Leondopulos, S.S.,
Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2012. Hippocampal networks on reliable
patterned substrates. J. Neurosci. Meth. 203:344-353.

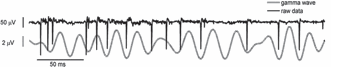 105. Leondopulos, S.S., Boehler, M.D.,
Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2012.
Chronic stimulation of cultured neural networks boosts oscillatory activity in
the beta and theta frequencies, J. Neural Eng. 9 026015 doi:10.1088/1741-2560/9/2/026015. PM:22361724
105. Leondopulos, S.S., Boehler, M.D.,
Wheeler, B.C., Brewer, G.J. 2012.
Chronic stimulation of cultured neural networks boosts oscillatory activity in
the beta and theta frequencies, J. Neural Eng. 9 026015 doi:10.1088/1741-2560/9/2/026015. PM:22361724
108. Brewer, GJ, Boehler, MD, Leondopulos, S, Pan, L, Alagapan, S, DeMarse, TB, Wheeler, BC. 2013. Toward a self-wired active reconstruction of the hippocampal trisynaptic loop: DG-CA3. Frontiers in Neural Circuits 7:165. PM:24155693 PMCID: 3800815
109. Pan L, Alagapan S, Franca E, DeMarse, T, Brewer GJ, Wheeler BC. 2014. Large extracellular spikes recordable from axons in microtunnels. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 22:453-459 PM:24240004 PMCID: PMC4013201
112. Pan L, Alagapan S, Franca E, Leondopoulos, S., DeMarse, T, Brewer GJ, Wheeler BC. 2015. An in vitro method to manipulate the direction and functional strength between neural populations. Frontiers Neural Circuits 9:32, doi: 10.3389/fncir.2015.00032 PM:26236198 PMID:26236198 Free PMC Article
114. DeMarse, TB, Pan, L, Alagapan, S, Brewer, GJ, Wheeler, BC (2016) Feed-Forward Propagation of Temporal and Rate Information between Cortical Populations during Coherent Activation in Engineered In Vitro Networks. Front Neural Circuits 10:32. PMID: 27147977 PMCID: PMC4840215
115. Bhattacharya, A., Desai, H., DeMarse, T.B., Wheeler, B.C. and Brewer, G.J. 2016. Repeating spatial-temporal motifs of CA3 activity dependent on engineered inputs from dentate gyrus neurons in live hippocampal networks. Front. Neural Circuits 10:45. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00045.doi PubMed PMID: 27445701; PMCID: 4923256.
116. Poli, D., Thiagarajan, S. DeMarse, T.B., Wheeler, B.C. and Brewer, G.J. 2017. Sparse and specific coding during information transmission between co-cultured dentate gyrus and CA3 hippocampal networks. Front Neural Circuits doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00013. PMCID: 5337490
117. Narula, U, Ruiz, A, McQuaide, M, DeMarse, TB, Wheeler, BC, Brewer, GJ (2017) Narrow microtunnel technology for the isolation and precise identification of axonal communication among distinct hippocampal subregion networks. PLoS One 12:e0176868. PMC5426613
118. Poli, D, Wheeler, BC, DeMarse, TB, and Brewer, GJ 2018. Pattern separation and completion of distinct axonal inputs transmitted via micro-tunnels between co-cultured hippocampal dentate, CA3, CA1 and entorhinal cortex networks. J. Neural Engineering. 15:046009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aabc20
Neuroscience of Aging and Alzheimer Disease
22. Brewer,
G.J. and Ashford, J.W. 1992. Human serum stimulates Alzheimer markers
in cultured hippocampal neurons. J.
Neurosci. Res. 33:355-369. PM:1335088
(AD has systemic markers).
38. Yang
Y., Quitschke, W.W. and Brewer, G. J. 1998. Upregulation of amyloid precursor
protein gene promoter in rat primary hippocampal neurons by phorbol
ester, IL-1 and retinoic acid, but not by reactive oxygen species. Molec. Brain
Res. 60:40-49.PM:9748493
(Genetic control of amyloid by
inflammatory mediators).
40. Brewer,
G.J. 1998. Age-related toxicity to
lactate, glutamate, and beta-amyloid in cultured adult neurons. Neurobiol.
Aging 19:561-568. PM:10192215
(Seminal basis for studying brain aging
in relation to Alzheimer’s disease).
44. Yang,
Y., Quitschke, W.W., Vostrov,
A.A. and Brewer, G.J. 1999. CTCF is essential for upregulating
expression from the amyloid precursor protein promoter during differentiation
of primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem.
73:2286-2298. PM:10582586
(Genetic control of amyloid expression).
55. Viel, J.J., McManus, D.J., Smith, S.H. and Brewer, G.J.
2001. Age and
concentration-dependent neuroprotection and toxicity by TNF in cortical neurons
from beta-amyloid. J. Neurosci. Res. 64:454-465.PM:11391700 (Early
identification of a role of inflammatory mediator TNF in exacerbating
beta-amyloid toxicity in AD)
59. Cady, C., Evans,
M.S. and Brewer, G.J. 2001. Age-related differences in NMDA responses in
cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res, 921:1-11. PM:11720706
60. Nathan, B.P.,
Jiang, Y., Wong, G.K., Shen, F., Brewer, G. and Struble, R.G. 2002.
Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits and apolipoprotein E3 promotes neurite
outgrowth in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons through the low-density
lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Brain Res. 928:96-105.PM:11844476
62. Patel, J.R.,
Brewer, G.J. 2003. Age-related changes in neuronal glucose uptake in response to
glutamate and beta-amyloid J. Neurosci. Res.72:527-536.PM:12704814
(Neuron glucose transport declines with
age to limit energy production, but the deficit is reversible).
69. Brewer, G.J.,
Lim, A., Capps, N.G., Torricelli, J.R. 2005. Age-related calcium changes,
oxyradical damage, caspase activation and nuclear condensation in hippocampal
neurons in response to glutamate and beta-amyloid, Exp. Gerontol., 40:426-437.PM:15919595
72. Brewer,G.J.; Reichensperger,J.D.;
Brinton,R.D. 2006. Prevention of age-related dysregulation
of calcium dynamics by estrogen in neurons, Neurobiology of Aging
27:306-317. PM:15961189
(Landmark age-related dysregulation of neuron calcium dynamics and reversal by
estrogen).
74. Parihar, M.S.,
Brewer, G.J. 2007a. Mitoenergetic
failure in Alzheimer disease. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 292 C8-C23 PM:16807300; http://ajpcell.physiology.org
75. Parihar,
M.S., Brewer, G.J. 2007b. Simultaneous
age-related depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased
mitochondrial ROS production correlate with age-related glutamate
excitotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons, J. Neuroscience Res. 85:1018-1032. PM:17335078. (First indication of age-related depolarization of neuron mitoochondria and relationship to oxyradical production).
81. Joseph, J.A.,
Carey, A., Brewer, G.J., Neuman, A., Lau, F.C.,
Fisher, D.R. 2007. Dopamine and
Aβ-induced stress signaling and decrements in Ca2+ buffering in
primary neonatal hippocampal cells are antagonized by blueberry extract. J. Alzheimer Dis. 11:433-446. PM:17656822
84. Parihar, M.S.,
Kunz, E., Brewer, G.J. 2008.
Age-related decreases in NAD(P)H and glutathione cause
redox declines before ATP loss during glutamate treatment of hippocampal
neurons. J. Neurosci.
Res. 86:2339-2352 PM:18438923.
(First evidence for
age-related deficits in redox state).
85. Patel, J.R.,
Brewer, G.J. 2008. Age-related
changes to TNF receptors affect neuron survival in the presence of
beta-amyloid. J. Neurosci. Res. 86:2303-2313 PM:18418902.
PMC2562897
(Further evidence for age-related role
of inflammatory cytokine TNF in synergistic enhancement of beta-amyloid
toxicity.)
87. Patel, J.R.,
Brewer, G.J. 2008. Age-related
differences in NFκB translocation and Bcl-2 ratio caused by TNFα and
Abeta42 promote survival in middle-age neurons and death in old neurons, Exp.
Neurol. 213:93-100. PM:18625500
PMC2597588
(Molecular basis for age-related
toxicity of TNF combined with beta-amyloid).
89. Jones, T.T. and
Brewer, G.J. 2009. Critical age-related loss of cofactors of
neuron cytochrome C oxidase reversed by estrogen. Exp. Neurology, 215:212-219. PM:18930048 PMCID:3018880 (First
identification of an age-related molecular deficit in neuron mitochondria AND
the potential for rapid reversal).
91. Brewer, G.J.
Lindsey, A.L. Kunz, E.Z.
Torricelli, J.R. Neuman, A. Fisher, D.R.
Joseph, J.A. 2010. Age-related toxicity of β-amyloid associated with
increased pERK and pCREB in
primary hippocampal neurons: reversal by blueberry extract. J. Nutr. Biochem. 21:991-998. PM:19954954 PMCID: 2891857
(Clear age-related induction of a stress
response by phytochemicals in blueberries to protect against beta-amyloid
toxicity.)
92. Brewer, G.J. 2010. Why vitamin E therapy fails for
treatment of Alzheimer disease. J.
Alzheimer’s Dis. 19: 27-30. PM: 20061623 PMCID: 3023173
 93. Jones, T.T. and Brewer, G.J. 2010. Age-related deficiencies in complex I
endogenous substrate availability and reserve capacity of complex IV in
cortical neuron electron transport.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenergetics, 1797:167-176. PMCID: PMC2812684. PMCID: 2812684
(Identification of the sites of
age-related dysfunction in mitochondria).
93. Jones, T.T. and Brewer, G.J. 2010. Age-related deficiencies in complex I
endogenous substrate availability and reserve capacity of complex IV in
cortical neuron electron transport.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenergetics, 1797:167-176. PMCID: PMC2812684. PMCID: 2812684
(Identification of the sites of
age-related dysfunction in mitochondria).
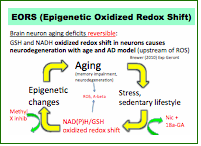
96. Brewer, GJ.
(2010) Epigenetic oxidative redox shift (EORS) theory of aging unifies the free
radical and insulin signaling theories, Exp Gerontol.45:173-179.
PM:19945522. PMCID: 2826600
(Potential new landmark theory of aging).
98. Joseph, J.A., Shukitt-Hale,
B., Brewer, G.J., Weikel, K.A., Kalt,
W., Fisher, D.R. 2010. Differential protection among fractionated blueberry polyphenolic families against DA-, Aβ42 and
LPS-induced decrements in Ca2+ buffering in primary hippocampal
cells. J. Agriculture Food Chem. 58:8196-8201. PM:20597478. (Polyphenolic fractions of blueberries are less effective than the whole for
neuroprotection.)
99. Struble, R.G.,
Ala, T., Patrylo, P.R., Brewer, G.J., Yan, X.X. 2010. Is brain amyloid production a
cause or a result of dementia of the Alzheimer type?,
J. Alz. Dis., 22:393-399. PM:20847431,
PMCID: 3079347
100. Parihar,
MS, Brewer, G.J. 2010. Amyloid beta as a modulator of synaptic plasticity, J. Alzheimer’s
Dis. 22:741-763. PM:20847424,
PMCID:
3079354 (Essential normal role of
A-beta is emphasized to raise caution about anti-amyloid therapies.)
101.
Barnett, A, Brewer GJ. 2011.
Autophagy in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: pathologic or protective? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 25: 385-394.PM:21422527
104. Walker,
MW, LaFerla, F; Oddo, S, and Brewer, GJ. Reversible
early age epigenetic histone modifications in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s
disease: effects on BDNF expression.
AGE, 35:519-531. Springer doi. PM:22237558,
(Major epigenetic changes in histone
acetylation and methylation occur early in aging and in 3xTg-AD mice, most
downloaded paper in Age 2012)
106. Ghosh, D;
LaFerla, F; Oddo, S., Brewer, GJ Oxidized redox state
in cultured hippocampal neurons precedes cognitive losses and macromolecular
ROS damage in 3xTg-AD mice. J. Neurosci. 32:5821-5832. PM:22539844, PMCID: 3376759 (An
early change in redox state, a metabolic shift, may be pathogenic.)
107. Ghosh, D.,
Brewer, GJ, 2013. Dual energy precursor and Nrf2 activator treatment additively
improves redox glutathione levels and neuron survival in aging and Alzheimer
mouse neurons upstream of ROS, Neurobiol.
Aging 35:179-190. (Redox state is
upstream of ROS for neurodegeneration and redox state can be targeted for
neuroprotection by boosting NADH synthesis and redox transcription.)
110. Ghosh, D., Brewer, GJ, 2014b. Relative importance of redox buffers GSH and NAD(P)H in age-related neurodegeneration and Alzheimer disease-like mouse neurons, Aging Cell 13:631-640. Doi: 10.1111/acel.12216, NIHMSID 571890. PM:24655393
111. Ghosh, D., Brewer, GJ, 2014c. External cys/cySS redox state modification controls the intracellular redox state and neurodegeneration via Akt in aging and Alzheimer’s mouse model neurons. J Alzheimer’s Dis 32:313-324. DOI 10.3233/JAD-132756 PM:24844688 NIHMSID 787070
113. LeVault, KR, Tischkau, S.A., Brewer, G.J. 2015. Circadian disruption reveals a correlation of an oxidative GSH/GSSG redox shift with learning and impaired memory in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 49:301-316. PM:26484899 NIHMSID 787138
119. Dong, Y, Digman, MA, Brewer, GJ 2019. Age- and AD-Related Redox State of NADH in Subcellular Compartments by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. GeroScience 41:51-67. PMID:30729413, PMC6423217
120. Dong, Y, Sameni, S., Digman, MA, Brewer, GJ. 2019. Reversibility of Age-related Oxidized Free NADH Redox States in Alzheimer’s Disease Neurons by Imposed External Cys/CySS Redox Shifts. Scientific Reports 9,11274.
Advances in Neuron Culture
23. Brewer, G.J.,
Torricelli, J.R., Evege, E.K. and Price, P.J. 1993. Optimized survival of hippocampal
neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal™, a new serum-free medium combination. J. Neurosci. Res. 35:567-576. PM:8377226
(The first culture medium optimized for
neurons. Remains the #1 neuron
culture medium with world-wide distribution through
license to Invitrogen)
24. Brewer, G.J.,
Torricelli, J.R., Evege, E.K. and Price, P.J. 1994. Neurobasal™ Medium/B27
supplement: a new serum-free medium
combination for survival of neurons.
Focus 16:(1)6-9.
25. Brewer, G.J. 1995. Serum-free B27/Neurobasal medium
supports differentiated growth of neurons from the striatum, substantia nigra, septum,
cerebral cortex, cerebellum and dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. Res. 42:674-683. PM:8600300
(Medium optimized for hippocampal
neurons supports the growth of neurons from many brain regions).
28. Brewer, G.J. and Price, P.J. 1996.
Viable cultured neurons in ambient carbon-dioxide and
hibernation storage for a month. Neuroreport 7:1509-1512. PM:8856709
(Invention that enabled the isolation of
adult neurons from brain and shipping live neurons world-wide.)
30. Brewer, G.J.
1997. Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons
of any age. J. Neurosci. Meth. 71:143-155. PM:9128149
(First demonstration of significant
viable recovery of adult neurons).
34. McManus, D.G. and
Brewer, G.J. 1997. Culture of neurons from postmortem rat
brain. Neurosci.
Lett. 224:193-196. PM:9131669 (Relationship
of post-mortem interval to neuron recovery.)
37. Evans,
M.S., Collings, M. and Brewer, G.J. 1998. Electrophysiology of embryonic, adult and aged rat hippocampal
neurons in serum-free culture.
J. Neurosci. Meth. 79:37-46. PM:9531458
39. Brewer G.J.,
Deshmane S. and Ponnusamy,
E. 1998. Precocious axons and improved survival
of rat hippocampal neurons on lysine-alanine polymer substrates. J. Neurosci.
Meth. 85:13-20.PM:9874136
43. Brewer, G.J. 1999. Regeneration and proliferation of
embryonic and adult hippocampal neurons.
Exp. Neurology 159:237-247. PM:10486191 (Early
work showing the plasticity of dedifferentiation and the induction of neuron
multiplication.)
45. Brewer, G.J.
June 1, 1999. Alternating lysine-alanine copolymer substrate for promoting
neuron survival and axon growth. United States Patent 5,908,783.
47. Brewer,
G.J. and Wallimann, T.W. 2000. Protective effect of the energy
precursor creatine against toxicity of glutamate and beta-amyloid in rat
hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 74:1968-1978. PM:10800940
52. Brewer, G.J. and
Price, P.J. January 30, 2001. Culture medium for maintaining
neural cells in ambient atmosphere, U.S. Patent 6,180,404. (Basis for Dr. Brewer’s company, BrainBits and source of $ millions of
income to the University).
53. Viel, J.J., McManus, D.J. and Brewer, G.J. 2001. Temperature and time
interval for culture of postmortem neurons from adult rat cortex. J. Neurosci. Res. 64:311-321.PM:11340637
56. Brewer G.J., Espinosa, J., McIlhaney, R., Pencek, T, Kesslak, J.P., Cotman, C.W., Viel, J.J., and McManus, D.Q. 2001. Culture and regeneration of human
neurons after brain surgery. J. Neurosci. Meth.
107:15-23.PM:11389937
61. Brewer, G.J.,
Espinosa, J.A., Struble, R.G. 2003. Effect of Neuregentmnutrient
medium on survival of cortical neurons after aspiration lesion in rats. J. Neurosurgery 98:1291-1298.PM:12816277
(Clear benefit of nutrient medium during
brain surgery).
65. Viel, J.J., McManus, D.J. and Brewer, G.J. 2004. Postmortem effect of pentobarbitol anaesthetic, Brain
Res. 1009:219-222. PM:15120600
66. Brewer, G.J.,
Jones, T.T., Walliman, T., Schlattner,
U. 2004 Higher respiratory rates and improved creatine stimulation in brain
mitochondria isolated with anti-oxidants, Mitochondrion 4:49-57 PM:16120374
78. Brewer, G.J., Le
Roux, P.D. 2007. Human primary brain tumor cell growth inhibition is serum-free
medium optimized for neuron survival, Brain Res. 1157:156-166. PM:17537410
79. Brewer, G.J., Torricelli, J.R. 2007. Isolation and culture of adult neurons
and neurospheres, Nature Protocols 2:1490-1498. PM:17545985 2007
Brewer Nat Prot.pdf (popular protocol that elicits inquiries
every week).